Awesome Github
A collection of cool hidden and not so hidden features of Git and GitHub. This cheat sheet was inspired by Zach Holman's Git and GitHub Secrets talk at Aloha Ruby Conference 2012 (slides) and his More Git and GitHub Secrets talk at WDCNZ 2013 (slides).
Shortlink: http://git.io/sheet
Read this in other languages: English, 한국어, 日本語, 简体中文, 正體中文.
GitHub Cheat Sheet is sponsored by Snapshot: create interactive professional-quality product photos using AI
Table of Contents
GitHub
Ignore Whitespace
Adding ?w=1 to any diff URL will remove any changes only in whitespace, enabling you to see only the code that has changed.
Read more about GitHub secrets.
Adjust Tab Space
Adding ?ts=4 to a diff or file URL will display tab characters as 4 spaces wide instead of the default 8. The number after ts can be adjusted to suit your preference. This does not work on Gists, or raw file views, but a Chrome extension can automate this.
Here is a Go source file before adding ?ts=4:

...and this is after adding ?ts=4:

Commit History by Author
To view all commits on a repo by author add ?author={user} to the URL.
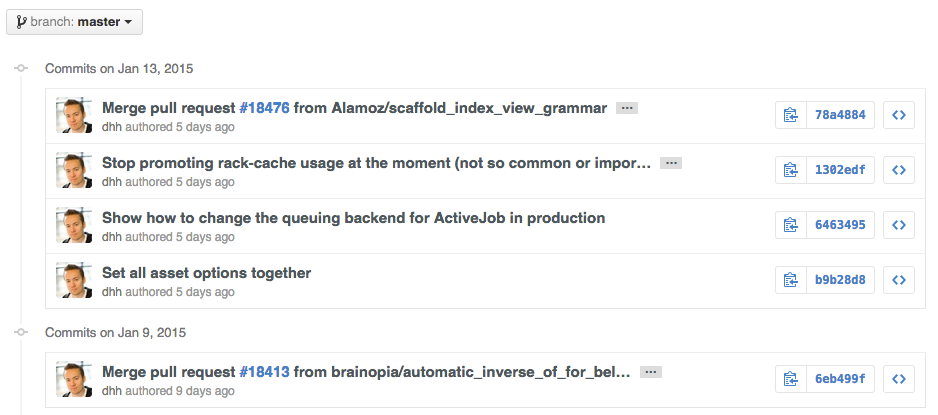
Read more about the differences between commits views.
Cloning a Repository
When cloning a repository the .git can be left off the end.
Read more about the Git clone command.
Branch
Compare all Branches to Another Branch
If you go to the repo's Branches page, next to the Commits button:
... you would see a list of all branches which are not merged into the main branch.
From here you can access the compare page or delete a branch with a click of a button.

Comparing Branches
To use GitHub to compare branches, change the URL to look like this:
where {range} = master...4-1-stable
For example:

{range} can be changed to things like:
Here, dates are in the format YYYY-MM-DD

Branches can also be compared in diff and patch views:
Read more about comparing commits across time.
Compare Branches across Forked Repositories
To use GitHub to compare branches across forked repositories, change the URL to look like this:
For example:

Gists
Gists are an easy way to work with small bits of code without creating a fully fledged repository.

Add .pibb to the end of any Gist URL (like this) in order to get the HTML-only version suitable for embedding in any other site.
Gists can be treated as a repository so they can be cloned like any other:

This means you also can modify and push updates to Gists:
However, Gists do not support directories. All files need to be added to the repository root. Read more about creating Gists.
Git.io
Git.io is a simple URL shortener for GitHub.

You can also use it via pure HTTP using Curl:
Keyboard Shortcuts
When on a repository page, keyboard shortcuts allow you to navigate easily.
Pressing
twill bring up a file explorer.Pressing
wwill bring up the branch selector.Pressing
swill focus the search field for the current repository. Pressing ↓ to select the “All GitHub” option changes the field to search all of GitHub.Pressing
lwill edit labels on existing Issues.Pressing
ywhen looking at a file (e.g.,https://github.com/tiimgreen/github-cheat-sheet/blob/master/README.md) will change your URL to one which, in effect, freezes the page you are looking at. If this code changes, you will still be able to see what you saw at that current time.
To see all of the shortcuts for the current page press ?:

Read more about search syntax you can use.
Line Highlighting in Repositories
Either adding, e.g., #L52 to the end of a code file URL or simply clicking the line number will highlight that line number.
It also works with ranges, e.g., #L53-L60, to select ranges, hold shift and click two lines:

Closing Issues via Commit Messages
If a particular commit fixes an issue, any of the keywords fix/fixes/fixed, close/closes/closed or resolve/resolves/resolved, followed by the issue number, will close the issue once it is committed to the repository's default branch.
This closes the issue and references the closing commit.

Read more about closing Issues via commit messages.
Cross-Link Issues
If you want to link to another issue in the same repository, simply type hash # then the issue number, and it will be auto-linked.
To link to an issue in another repository, {user}/{repo}#ISSUE_NUMBER, e.g., tiimgreen/toc#12.
Locking Conversations
Pull Requests and Issues can now be locked by owners or collaborators of the repo.

This means that users who are not collaborators on the project will no longer be able to comment.

Read more about locking conversations.
CI Status on Pull Requests
If set up correctly, every time you receive a Pull Request, Travis CI will build that Pull Request just like it would every time you make a new commit. Read more about how to get started with Travis CI.
Read more about the commit status API.
Filters
Both issues and pull requests allow filtering in the user interface.
For the Rails repo: https://github.com/rails/rails/issues, the following filter is built by selecting the label "activerecord":
is:issue label:activerecord
But, you can also find all issues that are NOT labeled activerecord:
is:issue -label:activerecord
Additionally, this also works for pull requests:
is:pr -label:activerecord
Github has tabs for displaying open or closed issues and pull requests but you can also see merged pull requests. Just put the following in the filter:
is:merged
Read more about searching issues.
Finally, github now allows you to filter by the Status API's status.
Pull requests with only successful statuses:
status:success
Read more about searching on the Status API.
Syntax Highlighting in Markdown Files
For example, to syntax highlight Ruby code in your Markdown files write:
This will produce:
GitHub uses Linguist to perform language detection and syntax highlighting. You can find out which keywords are valid by perusing the languages YAML file.
Read more about GitHub Flavored Markdown.
Emojis
Emojis can be added to Pull Requests, Issues, commit messages, repository descriptions, etc. using :name_of_emoji:.
The full list of supported Emojis on GitHub can be found at emoji-cheat-sheet.com or scotch-io/All-Github-Emoji-Icons. A handy emoji search engine can be found at emoji.muan.co.
The top 5 used Emojis on GitHub are:
:shipit::sparkles::-1::+1::clap:
Images/GIFs
Images and GIFs can be added to comments, READMEs etc.:
Raw images from the repo can be used by calling them directly.:

All images are cached on GitHub, so if your host goes down, the image will remain available.
Embedding Images in GitHub Wiki
There are multiple ways of embedding images in Wiki pages. There's the standard Markdown syntax (shown above). But there's also a syntax that allows things like specifying the height or width of the image:
Which produces:

Quick Quoting
When on a comment thread and you want to quote something someone previously said, highlight the text and press r, this will copy it into your text box in the block-quote format.
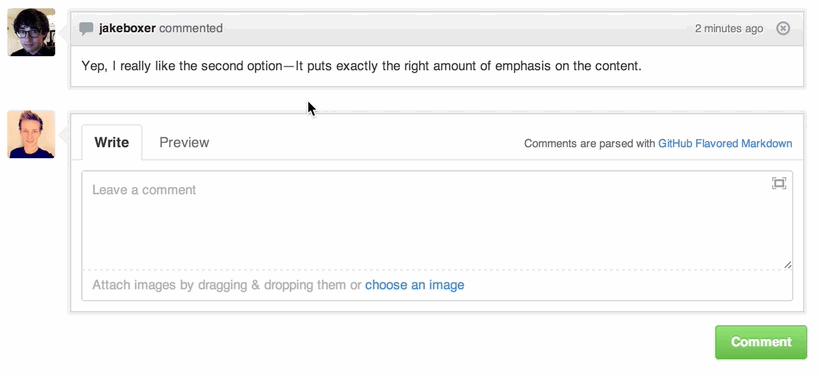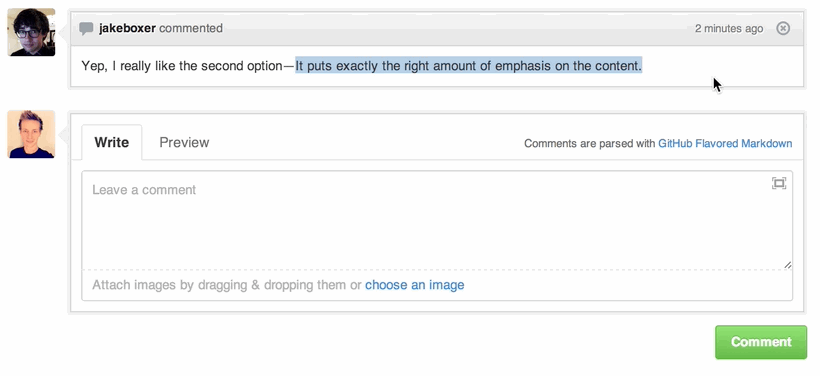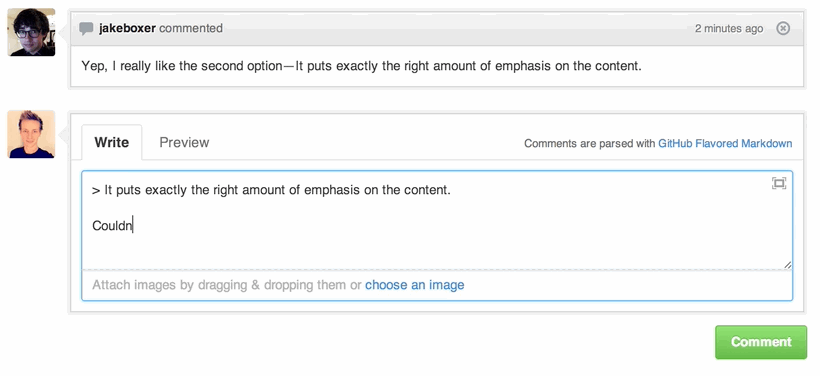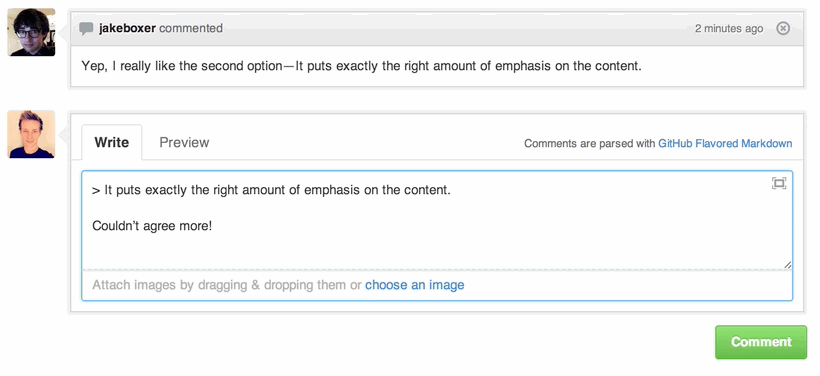
Read more about quick quoting.
Pasting Clipboard Image to Comments
(Works on Chrome browsers only)
After taking a screenshot and adding it to the clipboard (mac: cmd-ctrl-shift-4), you can simply paste (cmd-v / ctrl-v) the image into the comment section and it will be auto-uploaded to github.
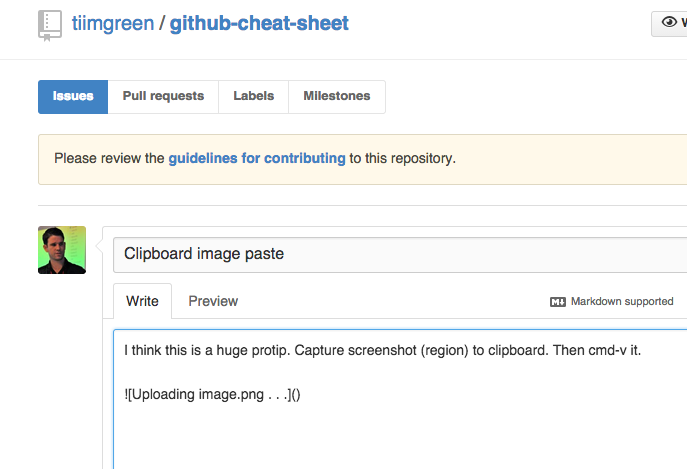
Read more about issue attachments.
Quick Licensing
When creating a repository, GitHub gives you the option of adding in a pre-made license:

You can also add them to existing repositories by creating a new file through the web interface. When the name LICENSE is typed in you will get an option to use a template:

Also works for .gitignore.
Read more about open source licensing.
Task Lists
In Issues and Pull requests check boxes can be added with the following syntax (notice the space):

When they are clicked, they will be updated in the pure Markdown:
Task Lists in Markdown Documents
In full Markdown documents read-only checklists can now be added using the following syntax:
Mars
Deimos
Phobos
Read more about task lists in markdown documents.
Relative Links
Relative links are recommended in your Markdown files when linking to internal content.
Absolute links have to be updated whenever the URL changes (e.g., repository renamed, username changed, project forked). Using relative links makes your documentation easily stand on its own.
Read more about relative links.
Metadata and Plugin Support for GitHub Pages
Within Jekyll pages and posts, repository information is available within the site.github namespace, and can be displayed, for example, using {{ site.github.project_title }}.
The Jemoji and jekyll-mentions plugins enable emoji and @mentions in your Jekyll posts and pages to work just like you'd expect when interacting with a repository on GitHub.com.
Read more about repository metadata and plugin support for GitHub Pages.
Viewing YAML Metadata in your Documents
Many blogging websites, like Jekyll with GitHub Pages, depend on some YAML-formatted metadata at the beginning of your post. GitHub will render this metadata as a horizontal table, for easier reading
Read more about viewing YAML metadata in your documents.
Rendering Tabular Data
GitHub supports rendering tabular data in the form of .csv (comma-separated) and .tsv (tab-separated) files.
Read more about rendering tabular data.
Rendering PDF
GitHub supports rendering PDF:

Read more about rendering PDF.
Revert a Pull Request
After a pull request is merged, you may find it does not help anything or it was a bad decision to merge the pull request.
You can revert it by clicking the Revert button on the right side of a commit in the pull request page to create a pull request with reverted changes to this specific pull request.
Read more about reverting pull requests
Diffs
Rendered Prose Diffs
Commits and pull requests, including rendered documents supported by GitHub (e.g., Markdown), feature source and rendered views.

Click the "rendered" button to see the changes as they'll appear in the rendered document. Rendered prose view is handy when you're adding, removing, and editing text:

Read more about rendered prose diffs.
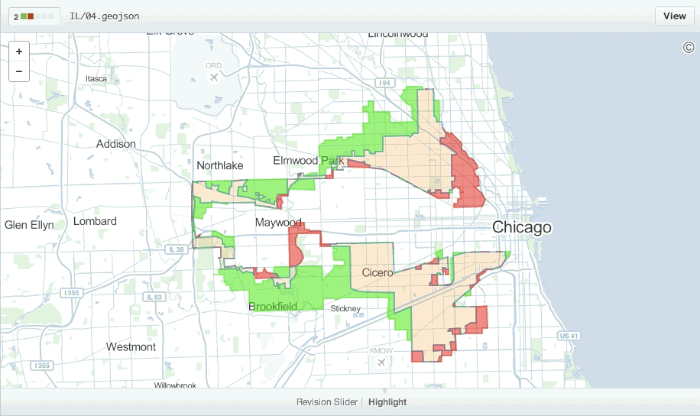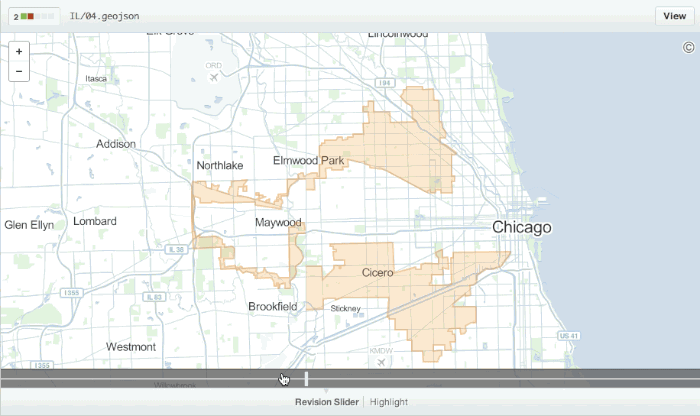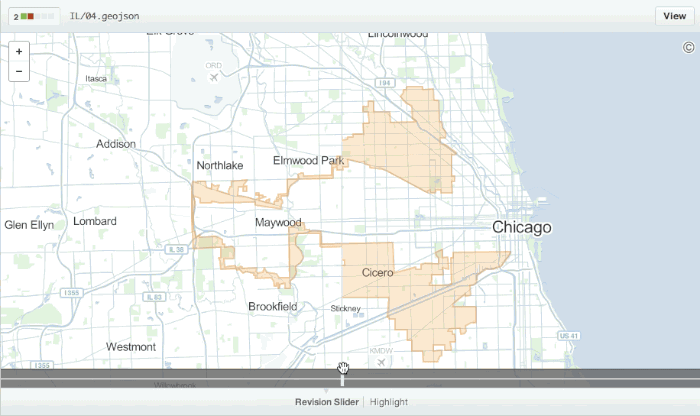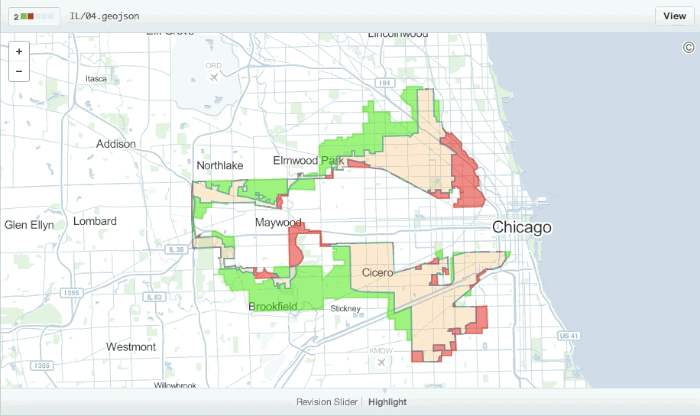
Diffable Maps
Any time you view a commit or pull request on GitHub that includes geodata, GitHub will render a visual representation of what was changed.
Read more about diffable maps.
Expanding Context in Diffs
Using the unfold button in the gutter of a diff, you can reveal additional lines of context with a click. You can keep clicking unfold until you've revealed the whole file, and the feature is available anywhere GitHub renders diffs.

Read more about expanding context in diffs.
Diff or Patch of Pull Request
You can get the diff of a Pull Request by adding a .diff or .patch extension to the end of the URL. For example:
The .diff extension would give you this in plain text:
Rendering and diffing images
GitHub can display several common image formats, including PNG, JPG, GIF, and PSD. In addition, there are several ways to compare differences between versions of those image formats.
Read more about rendering and diffing images.
Hub
Hub is a command line Git wrapper that gives you extra features and commands that make working with GitHub easier.
This allows you to do things like:
Check out some more cool commands Hub has to offer.
Contribution Guidelines
GitHub supports adding 3 different files which help users contribute to your project. These files can either be placed in the root of your repository or a .github directory under the root.
CONTRIBUTING File
Adding a CONTRIBUTING or CONTRIBUTING.md file to either the root of your repository or a .github directory will add a link to your file when a contributor creates an Issue or opens a Pull Request.
Read more about contributing guidelines.
ISSUE_TEMPLATE file
You can define a template for all new issues opened in your project. The content of this file will pre-populate the new issue box when users create new issues. Add an ISSUE_TEMPLATE or ISSUE_TEMPLATE.md file to either the root of your repository or a .github directory.
Read more about issue templates.

PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE file
You can define a template for all new pull requests opened in your project. The content of this file will pre-populate the text area when users create pull requests. Add a PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE or PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md file to either the root of your repository or a .github directory.
Read more about pull request templates.
Pull request template file generator
Octicons
GitHubs icons (Octicons) have now been open sourced.

Read more about GitHub's Octicons
GitHub Student Developer Pack
If you are a student you will be eligible for the GitHub Student Developer Pack. This gives you free credit, free trials and early access to software that will help you when developing.

Read more about GitHub's Student Developer Pack
GitHub Resources
GitHub Explore
https://github.com/explore
GitHub Blog
https://github.com/blog
GitHub Help
https://help.github.com/
GitHub Training
https://training.github.com/
GitHub Developer
https://developer.github.com/
Github Education (Free Micro Account and other stuff for students)
https://education.github.com/
GitHub Best Practices
GitHub Talks
How GitHub Uses GitHub to Build GitHub
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qyz3jkOBbQY
Introduction to Git with Scott Chacon of GitHub
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZDR433b0HJY
How GitHub No Longer Works
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gXD1ITW7iZI
Git and GitHub Secrets
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Foz9yvMkvlA
More Git and GitHub Secrets
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p50xsL-iVgU
SSH keys
You can get a list of public ssh keys in plain text format by visiting:
e.g. https://github.com/tiimgreen.keys
Read more about accessing public ssh keys.
Profile Image
You can get a user's profile image by visiting:
e.g. https://github.com/tiimgreen.png
Repository Templates
You can enable templating on your repository which allows anyone to copy the directory structure and files, allowing them to instantly use the files (e.g. for a tutorial or if writing boilerplate code). This can be enabled in the settings of your repository.

Changing to a template repository will give a new URL endpoint which can be shared and instantly allows users to use your repository as a template. Alternatively, they can go to your repository and click the 'Use as template' button.

Read more about using repositories as templates
Git
Remove All Deleted Files from the Working Tree
When you delete a lot of files using /bin/rm you can use the following command to remove them from the working tree and from the index, eliminating the need to remove each one individually:
For example:
Previous Branch
To move to the previous branch in Git:
Read more about Git branching.
Stripspace
Git Stripspace:
Strips trailing whitespace
Collapses newlines
Adds newline to end of file
A file must be passed when calling the command, e.g.:
Read more about the Git stripspace command.
Checking out Pull Requests
Pull Requests are special branches on the GitHub repository which can be retrieved locally in several ways:
Retrieve a specific Pull Request and store it temporarily in FETCH_HEAD for quickly diff-ing or merge-ing:
Acquire all Pull Request branches as local remote branches by refspec:
Or setup the remote to fetch Pull Requests automatically by adding these corresponding lines in your repository's .git/config:
For Fork-based Pull Request contributions, it's useful to checkout a remote branch representing the Pull Request and create a local branch from it:
Or should you work on more repositories, you can globally configure fetching pull requests in the global git config instead.
This way, you can use the following short commands in all your repositories:
Read more about checking out pull requests locally.
Empty Commits
Commits can be pushed with no code changes by adding --allow-empty:
Some use-cases for this (that make sense), include:
Annotating the start of a new bulk of work or a new feature.
Documenting when you make changes to the project that aren't code related.
Communicating with people using your repository.
The first commit of a repository:
git commit -m "Initial commit" --allow-empty.
Styled Git Status
Running:
produces:

By adding -sb:
this is produced:

Read more about the Git status command.
Styled Git Log
Running:
produces:

Credit to Palesz
This can be aliased using the instructions found here.
Read more about the Git log command.
Git Query
A Git query allows you to search all your previous commit messages and find the most recent one matching the query.
where query (case-sensitive) is the term you want to search, this then finds the last one and gives details on the lines that were changed.

Press q to quit.
Git Grep
Git Grep will return a list of lines matching a pattern.
Running:
will show all the files containing the string aliases.

Press q to quit.
You can also use multiple flags for more advanced search. For example:
-eThe next parameter is the pattern (e.g., regex)--and,--orand--notCombine multiple patterns.
Use it like this:
Read more about the Git grep command.
Merged Branches
Running:
will give you a list of all branches that have been merged into your current branch.
Conversely:
will give you a list of branches that have not been merged into your current branch.
Read more about the Git branch command.
Fixup and Autosquash
If there is something wrong with a previous commit (can be one or more from HEAD), for example abcde, run the following command after you've amended the problem:
Read more about the Git commit command. Read more about the Git rebase command.
Web Server for Browsing Local Repositories
Use the Git instaweb command to instantly browse your working repository in gitweb. This command is a simple script to set up gitweb and a web server for browsing the local repository.
opens:
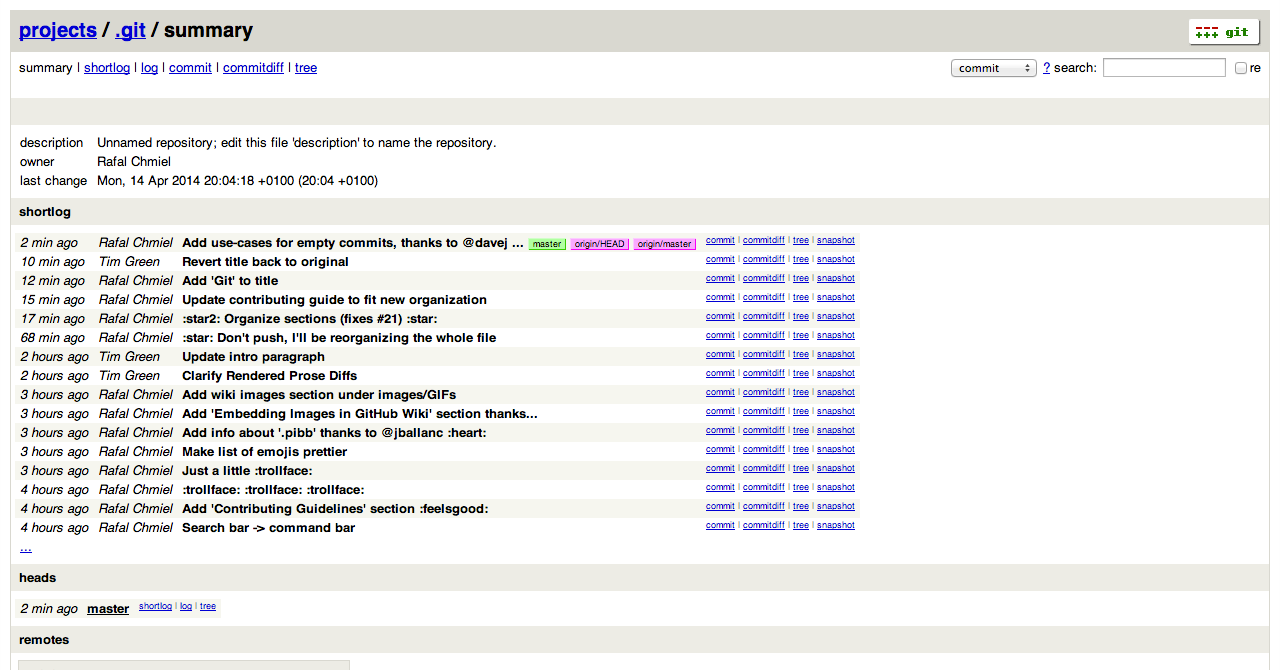
Read more about the Git instaweb command.
Git Configurations
Your .gitconfig file contains all your Git configurations.
Aliases
Aliases are helpers that let you define your own git calls. For example you could set git a to run git add --all.
To add an alias, either navigate to ~/.gitconfig and fill it out in the following format:
...or type in the command-line:
For example:
For an alias with multiple functions use quotes:
Some useful aliases include:
git cm
git commit
git config --global alias.cm commit
git co
git checkout
git config --global alias.co checkout
git ac
git add . -A git commit
git config --global alias.ac '!git add -A && git commit'
git st
git status -sb
git config --global alias.st 'status -sb'
git tags
git tag -l
git config --global alias.tags 'tag -l'
git branches
git branch -a
git config --global alias.branches 'branch -a'
git cleanup
git branch --merged | grep -v '*' | xargs git branch -d
git config --global alias.cleanup "!git branch --merged | grep -v '*' | xargs git branch -d"
git remotes
git remote -v
git config --global alias.remotes 'remote -v'
git lg
git log --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit --
git config --global alias.lg "log --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit --"
Some Aliases are taken from @mathiasbynens dotfiles: https://github.com/mathiasbynens/dotfiles/blob/master/.gitconfig
Auto-Correct
Git gives suggestions for misspelled commands and if auto-correct is enabled the command can be fixed and executed automatically. Auto-correct is enabled by specifying an integer which is the delay in tenths of a second before git will run the corrected command. Zero is the default value where no correcting will take place, and a negative value will run the corrected command with no delay.
For example, if you type git comit you will get this:
Auto-correct can be enabled like this (with a 1.5 second delay):
So now the command git comit will be auto-corrected to git commit like this:
The delay before git will rerun the command is so the user has time to abort.
Color
To add more color to your Git output:
Read more about the Git config command.
Git Resources
Official Git Site
http://git-scm.com/
Official Git Video Tutorials
http://git-scm.com/videos
Code School Try Git
http://try.github.com/
Introductory Reference & Tutorial for Git
http://gitref.org/
Official Git Tutorial
http://git-scm.com/docs/gittutorial
Everyday Git
http://git-scm.com/docs/everyday
Git Immersion
http://gitimmersion.com/
Git God
https://github.com/gorosgobe/git-god
Git for Computer Scientists
http://eagain.net/articles/git-for-computer-scientists/
Git Magic
http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~blynn/gitmagic/
Git Visualization Playground
http://onlywei.github.io/explain-git-with-d3/#freeplay
Learn Git Branching
http://pcottle.github.io/learnGitBranching/
A collection of useful .gitignore templates
https://github.com/github/gitignore
Unixorn's git-extra-commands collection of git scripts
https://github.com/unixorn/git-extra-commands
Git Books
Pragmatic Version Control Using Git
https://pragprog.com/titles/tsgit/pragmatic-version-control-using-git
Pro Git
http://git-scm.com/book
Git Internals PluralSight
https://github.com/pluralsight/git-internals-pdf
Git in the Trenches
http://cbx33.github.io/gitt/
Version Control with Git
http://www.amazon.com/Version-Control-Git-collaborative-development/dp/1449316387
Pragmatic Guide to Git
https://pragprog.com/titles/pg_git/pragmatic-guide-to-git
Git: Version Control for Everyone
https://www.packtpub.com/application-development/git-version-control-everyone
Git Videos
Linus Torvalds on Git
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4XpnKHJAok8
Introduction to Git with Scott Chacon
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZDR433b0HJY
Git From the Bits Up
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MYP56QJpDr4
Graphs, Hashes, and Compression, Oh My!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ig5E8CcdM9g
GitHub Training & Guides
https://www.youtube.com/watch?list=PLg7s6cbtAD15G8lNyoaYDuKZSKyJrgwB-&v=FyfwLX4HAxM
Git Articles
GitHub Flow
http://scottchacon.com/2011/08/31/github-flow.html
Migrating to Git Large File Storate (Git LFS)
http://vooban.com/en/tips-articles-geek-stuff/migrating-to-git-lfs-for-developing-deep-learning-applications-with-large-files/
Github-VPS

📜 Description
GitHub Codespaces allows developers and hackers to create and utilize their coding environments directly from GitHub in the cloud. As a CTF player or pentester, you can also leverage GitHub Codespaces similarly to a VPS (Virtual Private Server). This makes it easy to work on projects from anywhere with the flexibility of a portable development setup using Docker.
📚 Table of Contents
🙍🏻♂️ Configuration
👨🏾⚖️ License
🔥 What's Nice
Offers more power with
2-vCPUs,8GB-RAM, and a temporary32GB-SSDstorage drive.Higher performance with
4-vCPUs,16GB-RAM, and a temporary32GB-SSDstorage drive.
🐳 Installation
[!NOTE] Github codespace terminal

Kali headless vs default
kali-linux-default: This is a metapackage that installs the default set of tools for a typical Kali Linux system. It includes both GUI and command-line tools that are generally used for penetration testing and security auditing.It is intended for users who want the full range of Kali Linux tools, including the graphical user interface (GUI) tools and a more complete desktop experience.
kali-linux-headless: This is another metapackage, but it installs a more minimal setup. It is intended for users who do not need or want a graphical user interface (GUI). This package installs the core tools needed for penetration testing, but without the overhead of a GUI environment (like X11 or a desktop environment).It’s ideal for servers or systems where you want to run Kali in a headless environment (no monitor, no graphical interface).
Key Differences
kali-linux-default includes the full Kali suite with a GUI.
kali-linux-headless includes the same core set of tools, but without the GUI, making it lighter and more suitable for headless (non-GUI) environments.
Which one to use?
If you plan to use Kali Linux with a graphical interface (for example, on a laptop or desktop), go with kali-linux-default.
If you plan to run Kali on a server or in a virtual machine where you don’t need a GUI, choose kali-linux-headless for a more lightweight installation.
Installation without errors
[!TIP] Refer to default installation Guide
Configuration
Starting Docker Kali Image
Adding non-root user

Diskspace Monitoring
Docker Privileged
[!IMPORTANT] The way to use openvpn or enable
tun0you need to add--privilegedoption instead using--ttyby default, Docker containers do not have access to TUN/TAP devices on the host system due to security and isolation concerns.
Automation in new terminal session
kali_privs.sh
New Terminal Session
[!NOTE] Github codespace terminal
Adding Graphical User Interface (noVNC)
[!IMPORTANT] Run this script in the terminal of your Github Codespace, which is using Ubuntu OS
setup-noVNC.sh
Starting noVNC Web access
start-novnc.sh
🚫 Temporarily Disabled
If you've used 100% of the included services for GitHub Codespaces storage, a few things might happen depending on your account settings and actions.
Inability to Use Codespaces: You won't be able to create or use GitHub Codespaces until either your
free allotment resets next monthor you take action to manage your usage.Options to Regain Access:
Set Up a Spending Limit: You can set up a
spending limiton your GitHub account to prevent unexpected charges and manage your usage effectively.Delete Unused Resources: Consider
deleting Codespacesorprebuildsthat are no longer needed to free up space and potentially reduce future charges.
Access to In-Progress Work: It's important to
exportany unpushed work to a branch if you want to retain access to your in-progress projects. This ensures you have a backup and can continue working on them when you regain access to Codespaces.Review Usage and Charges: GitHub provides a
usage reportwhere you can see detailed information about your Codespaces and prebuild usage. This can help you understand your usage patterns and manage future usage effectively.


🔄 Changelog
v1.1.0 - [2024-06-29]
Adjustment:
Adding
privilegeduser mode to enable TUN error when starting the OpenVPN file.
📝 Todo
Adding remotehost for graphical user inferface (GUI), this includes xrdp, ssh, noVNC and etc.Adding Automated builds Dockerfile to ensure consistency and reliability.
Adding ngrok to exposed your cloud servers behind NATs and firewalls to the public internet over secure tunnels.
Adding Openvpn default configuration to ensure privacy and security
👨🏾⚖️ License
This project is under terms of the MIT License. bugs and error, create issue
Last updated